字数:
本文主要讨论以下几个问题:
- 跨域现象的简单描述
- 跨域问题的解决办法(非全面)
- 跨域解决办法在实际中的应用
跨域现象的简单描述
跨域是浏览器的同源策略引发的一个问题,主要是为了安全角度考虑,防止跨站攻击。现象非常地简单,现在做两个网站,一个是t2.tao.de,见章,另一个是t1.tao.de,这第二个站点可以做得非常地简单,一个静态表单就可以了:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://www.w3school.com.cn/jquery/jquery-1.11.1.min.js">
</script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#submit").click(function(){
alert($("input[name='user']").val());
$.post("http://t2.tao.de/add_user" );
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" value="asdasd" name="user"/><input id="submit" type="submit" value="submit"/>
</body>
</html>
显然,在t1站点上提交一个ajax的POST请求到t2,看是否能成功,结果显示如下:
Failed to load http://t2.tao.de/add_user: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource. Origin 'http://t1.tao.de' is therefore not allowed access.
结果表明,t1是被禁止掉了。解决办法有好几种,比如JSONP以及CORS,下文仅介绍在服务器反反代理的解决办法。
跨域问题的解决办法
同源策略提到了,访问不同的域名或端口,即跨域了,那么其中的一个解决办法就是让访问的域名相同即可,比如上文,t1的页面要访问t2的接口,那么能不能把t1的页面变成t2的?
通过Nginx的反代理配置是很容易做到的:
server {
listen 80;
server_name t2.tao.de;
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|html)$ {
#root /var/www/web/t1/;
proxy_pass http://t1.tao.de;
index index.html;
}
location / {
proxy_set_header Host t2.tao.de;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
}
}
这个nginx的配置即将静态页反代理到站点1,因此访问http://t2.tao.de/index.html,其内容来自于t1。
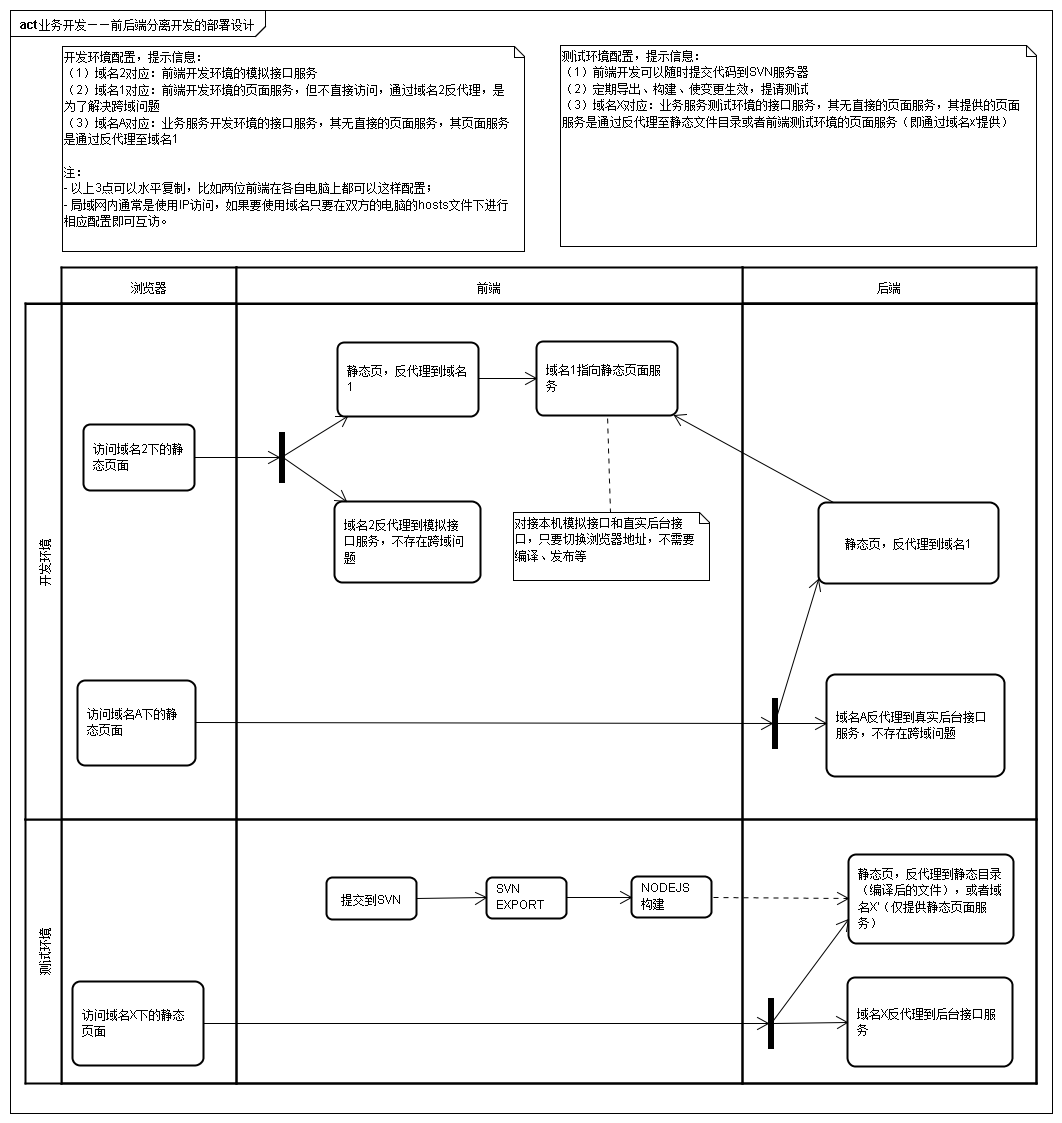
实际应用
以上做法是非常的简单,实际运用起来作用颇大,以下是一个运用场景,搭建前后端分离开发的Developement环境的示意图: